The Importance of Prenatal DNA Testing
Prenatal DNA testing is a valuable tool that can provide crucial information about a baby’s genetic makeup before birth. This type of testing involves analyzing the DNA of the fetus to determine paternity, screen for genetic disorders, and assess other genetic characteristics.
Benefits of Prenatal DNA Testing
One of the key benefits of prenatal DNA testing is the ability to establish paternity with a high degree of accuracy. This can be important for legal reasons, as well as for personal peace of mind. Knowing the biological father of a child can help in making important decisions regarding custody, support, and family relationships.
In addition to paternity testing, prenatal DNA testing can also screen for genetic disorders that may be present in the fetus. Early detection of these disorders can allow parents to prepare for any necessary medical interventions or treatments after the baby is born.
Methods of Prenatal DNA Testing
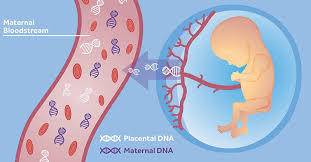
There are several methods used for prenatal DNA testing, including non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), chorionic villus sampling (CVS), and amniocentesis. NIPT is a simple blood test that analyzes fetal DNA circulating in the mother’s bloodstream, while CVS and amniocentesis involve sampling cells from the placenta or amniotic fluid.
Considerations for Prenatal DNA Testing
It is important to consider both the benefits and risks associated with prenatal DNA testing before deciding to undergo the procedure. While these tests can provide valuable information, they also carry a small risk of miscarriage or other complications. It is essential to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider and make an informed decision based on individual circumstances.
Conclusion
Prenatal DNA testing offers valuable insights into a baby’s genetic makeup and can help parents make informed decisions about their child’s health and well-being. By understanding the benefits and considerations associated with these tests, expectant parents can navigate this process with confidence and clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions About Prenatal DNA Testing
- What is prenatal cell-free DNA for?
- What is prenatal DNA?
- How to do a prenatal DNA test?
- How accurate is a prenatal DNA test?
What is prenatal cell-free DNA for?
Prenatal cell-free DNA testing, also known as non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), is a screening method used to analyze fetal DNA present in the mother’s bloodstream during pregnancy. This type of testing is primarily used to screen for certain genetic conditions and chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, such as Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13. Prenatal cell-free DNA testing offers expectant parents a non-invasive way to obtain valuable information about their baby’s health and genetic makeup early in pregnancy, allowing for informed decision-making and appropriate medical management if necessary.
What is prenatal DNA?
Prenatal DNA refers to the genetic material present in an unborn baby before birth. Prenatal DNA testing involves analyzing this genetic material to determine various aspects such as paternity, genetic disorders, and other genetic characteristics of the fetus. This testing can provide valuable information to expectant parents about the baby’s health and genetic makeup even before they are born. Understanding prenatal DNA is essential for making informed decisions regarding the well-being of the child and preparing for any potential medical interventions or treatments that may be necessary after birth.
How to do a prenatal DNA test?
To conduct a prenatal DNA test, there are several methods available depending on the stage of pregnancy and the specific needs of the parents. Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is a common method that involves a simple blood draw from the mother to analyze fetal DNA circulating in her bloodstream. Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis are more invasive procedures that involve sampling cells from the placenta or amniotic fluid, respectively. These tests are typically performed by healthcare professionals in specialized clinics or hospitals. It is important for expectant parents to consult with their healthcare provider to determine the most suitable method for their individual circumstances and to understand the risks and benefits associated with each option before proceeding with prenatal DNA testing.
How accurate is a prenatal DNA test?
The accuracy of a prenatal DNA test is typically very high, with results often exceeding 99% accuracy for paternity testing. Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) using maternal blood samples has shown to be highly accurate in determining genetic information about the fetus. However, it is important to note that the accuracy of prenatal DNA testing can vary depending on the method used and other factors such as sample quality. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider or genetic counselor to understand the specific accuracy rates associated with the chosen prenatal DNA testing method and any potential limitations.
